How to Do Keyword Research in 2025: Ultimate Guide
How to Do Keyword Research in 2025: Ultimate Guide
Keyword research is one of those essential skills everyone in digital marketing circles learns and hones, but few truly master. As 2025 brings fresh challenges and opportunities—from AI-powered search engines to shifting user behaviours—staying at the front means refining your approach. Whether you’re tackling your first SEO campaign or aiming to upend your competitors, the right techniques and mindset can make all the difference.
Let’s walk through strategies and subtle tactics that matter now, and will continue to matter as search evolves. Fasten your seatbelt: you’re about to rethink how you gather, analyse, and act on keyword possibilities.
Why Keyword Research Still Matters
It might seem like all the focus has moved towards content quality, and social signals, and technical SEO. While those absolutely count, none of your other efforts land unless you understand what your audience is typing, asking, and looking for.
Good keyword research doesn’t just help you attract the right people. It gives sharp insights about the language your audience uses, their intent, and even their worries or dreams. When you sync your website’s words with what people search, not only will you rank better, but engagement rates soar as well.

Image Source: thrive themes
Modern Tools of the Trade
A strong toolkit is your best friend. Today, there are so many free and paid tools, each bringing unique advantages. Here’s a quick comparison of some of the most useful platforms for keyword discovery in 2025.
| Tool | Best For | Main Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Keyword Planner | Baseline research, Ad campaigns | Historical trends, forecasts, ad data | Free (with account) |
| Ahrefs | Competitive analysis, difficulty | Keyword Explorer, SERP history, Click data | $$ |
| SEMrush | Content gap, global data | Keyword Magic Tool, topic clusters | $$ |
| Moz | Keyword suggestions, easy UX | Keyword Difficulty, Priority scoring | $ – $$ |
| Answer The Public | Question-based research | Visual data, autocomplete phrases | Limited free/$ |
| ChatGPT/Bard | Ideation, long-tail suggestions | Conversational ideas, synonyms | Free/Paid |
Different tools excel in different areas. Mixing a few often brings the best results, as it reduces blind spots in your research.
How to Do Keyword Research Step by Step
Moving beyond “pop a seed keyword into a tool and export,” let’s unpack the key stages to arriving at a set of truly valuable keywords.
1. Define Your Goals
Start with big-picture clarity. Are you focused on lead generation, ecommerce sales, brand awareness, or something else entirely? Your KPIs will influence the kind of keywords you need. For an online store, that means lots of product- or solution-aware terms. A SaaS company might lean into educational phrases.
2. Brainstorm Seed Keywords
Pull together a list of seed terms that describe your offering. Tap into:
- Your own product names or categories
- Frequently asked customer questions
- Related brands or competitors
- Industry lingo and jargon
Include various ways people express the same thing, spelling variations, and even common misspellings. This helps capture real-life search patterns, not just what looks good on paper.

3. Expand Ideas with Keyword Tools
Armed with your seed list, dive into your chosen research platforms. Instead of sticking to one, extract lists from at least two or three different tools. Look for:
- Suggestions based on your seed keywords
- Autocomplete predictions from Google
- ‘People also ask’ and related searches
- Trending questions from community sites (Reddit, Quora, etc.)
Stacking your lists exposes you to unexpected variations you might have missed otherwise.
Expand Ideas with Keyword Tools using SEMrush:
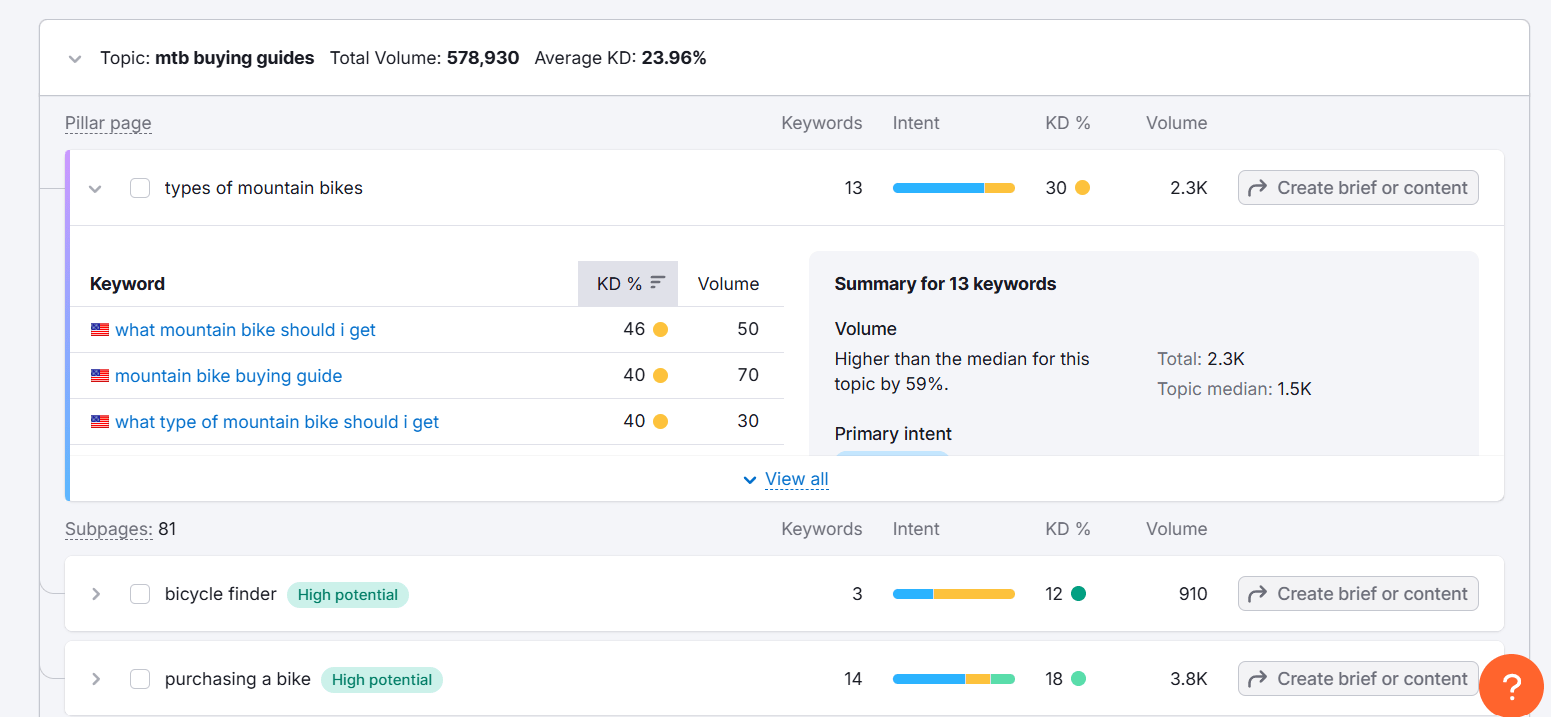
4. Segment by Search Intent
Intent is everything now. Gone are the days of chasing pure volume. Classify keywords by what the searcher really wants:
- Informational (how, what, who, guide to…)
- Navigational (brand names, product lines)
- Transactional (buy, best price, order now)
- Commercial investigation (review, comparison, top 10…)
This intent-based grouping lets you match specific keywords to the right content type, increasing both your ranking chances and conversion potential.

5. Analyse Search Volume, Competition, and Trends
Not all high-volume keywords are worth chasing; not all low-volume ones should be ignored. Pay attention to a blend of:
- Monthly search volume (from Google or third parties)
- Keyword difficulty or competitive scores (each SEO tool calculates this differently)
- Seasonality and trend curves (Google Trends is your ally)
Spikes in interest around certain times—holidays, events, product launches—can create opportunities if you prepare ahead.
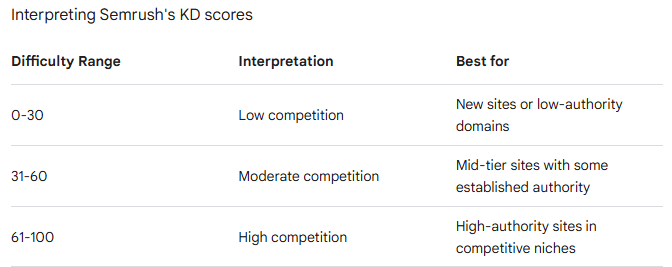
For a new website is not a good idea to start with a really high KD you needs to find a balance between KD and traffic
6. Find the ‘Low-Hanging Fruit’
Experienced SEOs know that quick wins often come from “medium” or “long tail” keywords. These usually:
- Have modest but consistent search volume
- Face limited competition (no big brands dominating page one)
- Are highly specific, aligning closely with buyer intent
Sprinkle your list with a hefty proportion of these to see earlier traffic returns and faster improvement. You also need to consider the differences across industries. Some niches naturally have lower overall traffic but much higher average order values. That’s why keyword difficulty (KD) and traffic metrics shouldn’t be judged by a fixed formula—it’s not as simple as saying KD 10 with 100 searches is good, or KD 40 with 1,000 searches is bad.
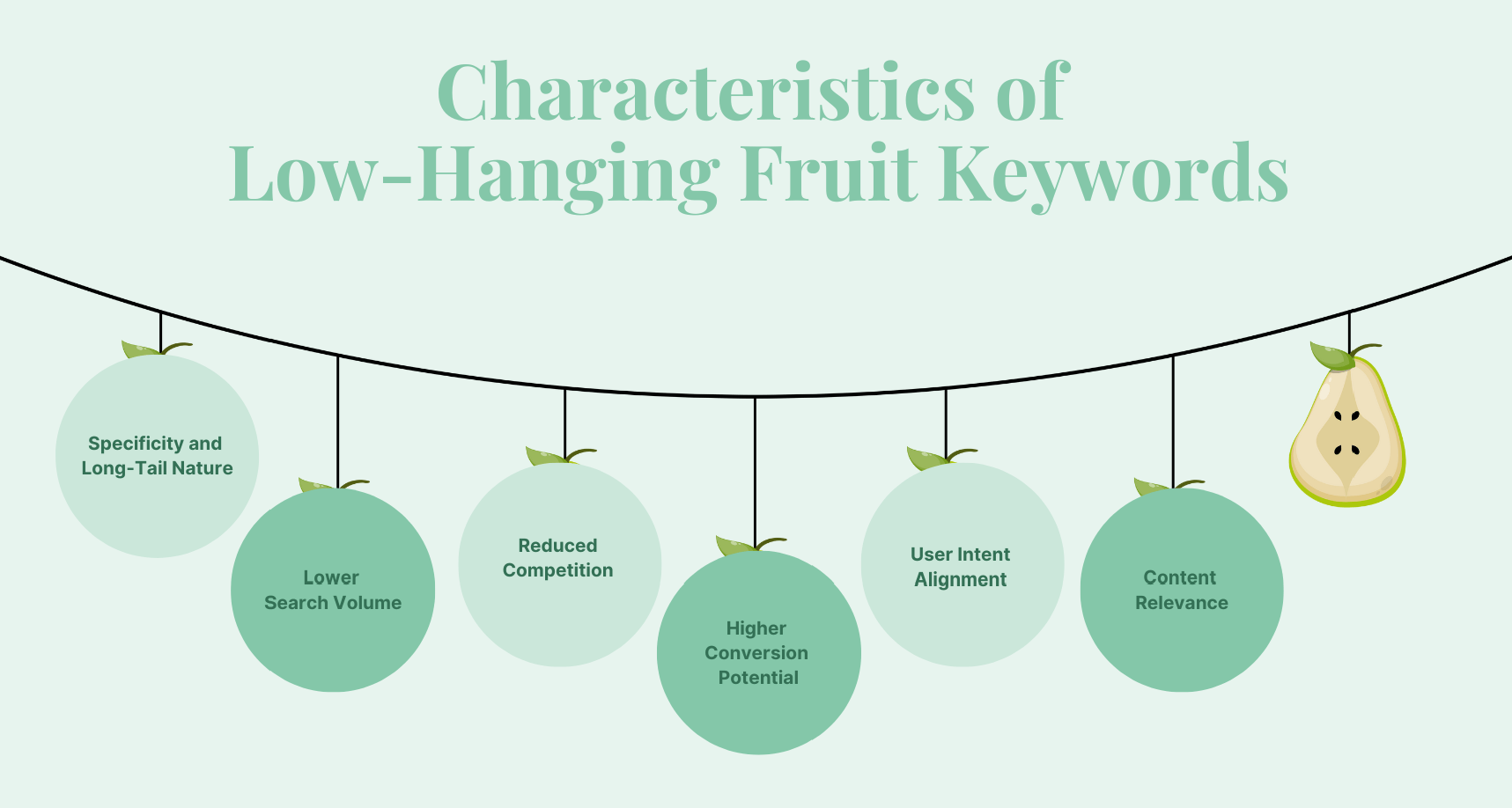
Image Source: sortlist
7. Evaluate SERPs with a Human Eye
Raw data is useful, but looking up actual results for a keyword can be even more revealing. Search your target keywords and take note of:
- What kind of results dominate (blog posts, videos, product listings, forums)?
- Are Google ads pushing organic results down?
- Are there a lot of featured snippets, local packs or images?
- What’s the average content length and format?
This real-world research steers your content planning to fit what Google is already favouring.
8.Optimising for Zero-Click Search Results
Not every search leads to a click anymore. In 2025, a growing share of queries are resolved directly on the SERP through featured snippets, People Also Ask (PAA) boxes, knowledge panels, and other zero-click formats. While this might seem like a loss of traffic, it’s actually an opportunity to claim premium real estate and boost brand visibility—if you know how to play the game.
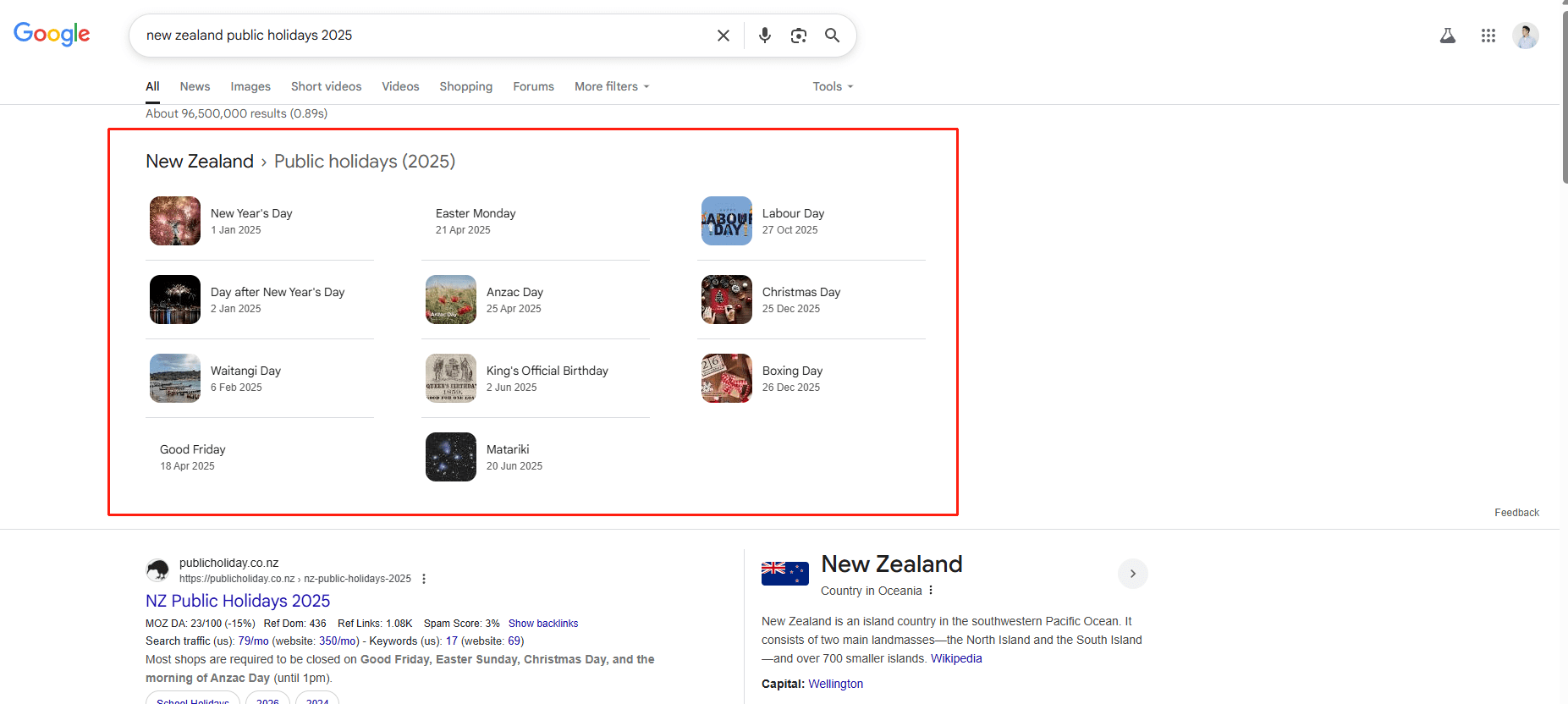
What Types of Keywords Trigger Zero-Click Results? Short, factual, or question-based queries are most likely to show instant answers. Think: “What is ROI?”, “New Zealand public holidays 2025”, or “best time to post on Instagram.” These are often targeted by Google’s featured snippets or PAA sections.
How to Optimise for Them? Structure is everything. Use headers that reflect actual search queries and provide short, direct answers (ideally 20–40 words) immediately below. For example, lead your content with a one-sentence definition or step-by-step list before diving into deeper explanations. This formatting makes your page a strong candidate for snippet selection.
Additionally, include FAQ-style content with schema markup like FAQPage, and write in a tone that aligns with the “instant answer” mindset—clear, scannable, and precise.
Why It Matters Even if users don’t click through, appearing in these areas builds brand credibility, increases trust, and puts your content ahead of traditional organic listings. It’s also a stepping stone to voice assistant results, which often pull from featured snippet content.
Example of a Zero-Click search results:
9. Organise and Prioritise
A list of 500 potential keywords isn’t much help unless it’s structured. Filter, tag, and sort them by:
- Intent
- Difficulty
- Priority (alignment with goals)
- Potential traffic impact
Consider tools like Google Sheets, Airtable, or even specialist SEO software to keep your keyword treasure trove accessible and actionable.
Going Further with Advanced Tactics
Seasoned marketers in 2025 are using a few extra moves for an edge.
Topical Authority Building
Just ranking for single keywords is yesterday’s news. Now, Google rewards sites with cohesive ‘topic clusters.’ That means mapping your keywords to interconnected articles, guides, and resources—proving you’re the expert, not just a lucky one-time result.
How to do this:
- Group closely related queries under ‘pillar’ subjects.
- Plan supporting pieces that link back to this pillar.
- Always target a mix of broad and narrow terms.
Incorporating AI-Generated Suggestions
ChatGPT, Google Bard, and similar tools are surprisingly good at surfacing long-tail and question-based keywords humans might overlook. Ask AI to simulate customer queries, brainstorm buying questions, or suggest layman’s ways to phrase technical language.
User Behaviour Insights
Keyword stats only reveal half the story. Using Google Analytics, Search Console or even session replay tools, look at:
- What searches already bring traffic?
- Which pages people bounce from (did the keyword fit the content)?
- Internal search queries on your site
Reverse-engineering from existing data leads to more grounded keyword choices.
Semantic Intent Mapping & Multimodal Search Optimization
In 2025, search engines increasingly prioritize meaning over exact keywords. Instead of matching literal terms, modern systems interpret user intent using deep semantic understanding—mapping queries to concepts, entities, and context across multiple modalities (voice, text, image, video) . Google’s evolving algorithms like MUVERA and SGE operate across multi-vector embeddings, enabling them to parse and respond to user needs more accurately than ever before .
Why Multimodal Optimization Matters
Search is no longer limited to text input. Users ask questions via voice, use images to search, and expect smart, AI-driven visual responses. According to recent trends:
- Over 65% of adults use voice-enabled devices regularly for search.
- Google Lens handles nearly 20 billion visual searches each month, with a significant portion tied to shopping or identification tasks .
How to Optimize for Semantic & Multimodal Search
1. Map Queries by Intent, Not Just Keywords
- Analyze search behavior to classify micro-intents—such as immediate purchase need, comparison, or local inquiry—as part of Search Intent 3.0.
- Use NLP and vector embedding tools to cluster keywords based on semantic relationships rather than frequency alone .
2. Create Content That Speaks Across Modalities
- Embed video, images, infographics, and voice-friendly content alongside your text.
- Add ImageObject and VideoObject schema markup for better visibility in visual-based search results .
- Use structured data such as FAQPage, HowTo, and Speakable to help AI systems interpret your content for voice assistants and visual summarization .
3. Build Topical Entity Clusters
- Develop pillar content focused on key entities, supported by cluster pages that explore related subtopics. Internal linking reinforces semantic relationships .
- Consistent use of entity-based schema helps Google link your content into its internal knowledge graph.
4. Emphasize Trust and User Intent Signals
- AI models like MUVERA and Google Gemini use intent understanding, structured content, and E-E-A-T signals to evaluate quality and relevance .
- Boost trust indicators: author credentials, expert quotes, citations from reputable sources, and site usability signals like dwell time and scroll depth .
Benefits of Semantic & Multimodal Optimization
By adopting this approach, content becomes more:
- Discoverable via voice, image, or video searches alongside traditional typing queries.
- Trusted & contextually aligned with user needs and the underlying intent of their queries.
- AI-friendly, increasing the chances of being included in AI-generated overviews or conversational replies.
Predictive & Trend‑Based Keyword Research
In an era where AI analyzes massive datasets and user behaviours shift rapidly, traditional keyword research—based on static, historical data—is no longer enough. Predictive keyword research uses AI-powered insights to forecast emerging trends and search behaviours before they fully materialise. This allows you to create content proactively, gaining visibility ahead of competitors. By 2025, AI-driven predictive tools are reshaping how marketers anticipate topics, timing, and intent—and those who leverage them stay ahead of the curve
Core Concepts & Methodologies
- AI‑Driven Forecasting Modern tools analyze past volume, related term spikes, and competitor activity to predict which keywords will surge next. This enables content planning before a term becomes competitive, giving early-mover advantage.
- Semantic Clustering & Intent Prediction AI can group keywords semantically—clustering terms by concept and intent—rather than just frequency. This helps you build topic clusters aligned with future search needs, not just past popularity.
Practical Tactics to Implement
- Monitor Google Trends with AI Tools Identify rising interest for specific queries or topics—especially those that show upward momentum—to act early.
- Use Predictive SEO Platforms Platforms like AI-based keyword discovery and forecasting tools can highlight high-potential keywords before they spike. Track expected search volume growth and adjust your content calendar accordingly, especially for seasonal or event-related terms.
- Audit Competitor Moves Analyze competitors ranking for rapidly-growing terms and identify gaps—topics or subqueries they’re missing—to capture rising demand ahead of them.
- Plan Content Proactively Map predicted trends into your content roadmap. For instance, if AI forecasts a surge in interest for “post-COVID remote work solutions” in Q3, prepare or refresh related pillar pages and blog content beforehand.
- Validate and Iterate Quarterly Compare predictions with actual search behaviour and adjust strategies. This iterative approach refines accuracy and helps avoid over-investment in trends that don’t take off.
Benefits of This Strategy
- Early Visibility & First-Mover Advantage Being present as a topic gains traction can lead to strong rankings with less competition initially.
- Optimised Resource Allocation Focus your efforts where they are likely to pay off fastest, rather than chasing high-volume but saturated keywords.
- Alignment with Emerging User Intent As search queries evolve, your content remains relevant and ahead of demand rather than trailing it.
Voice Search & Natural‑Language Long‑Tail Keywords
Voice search has rapidly transformed how people find information online. Rather than typing concise phrases like “best plumber,” users now ask full-sentence, conversational questions such as “Where can I find a reliable plumber nearby today?” These spoken queries are more specific, more natural, and reflect higher intent. As a result, traditional short keywords are often insufficient; voice search demands long-tail, natural-language phrases that mirror everyday speech.
Key Strategies to Optimize for Voice Search
- Target conversational long-tail keywords
- Focus on question-based queries that reflect how people speak: “How do I…?”, “Where can I…?”, “Who is the best…?”
- Use tools like Google’s “People Also Ask” and AnswerThePublic to identify real-world phrasing you can directly address.
- Create FAQ-style content
- Structure your content around real questions relevant to your audience. Each question should appear as a heading, followed by a concise, informative answer.
- This format aligns well with how voice assistants retrieve and read out answers.
- Use structured markup where appropriate
- Apply schema such as FAQPage or Speakable to help search engines identify the most relevant answer segments. This increases the chance your content will be read aloud by voice assistants.
- Write in a conversational tone
- Avoid formal or technical language. Use contractions and simple expressions that feel natural in spoken conversation.
- For example, instead of “Our store operates between 9 and 5,” say “We’re open from 9 AM to 5 PM—just in case you want to stop by before closing.”
- Optimize for local voice queries
- Many voice searches are location-based (“near me” queries). Ensure your site includes location-specific pages, mentions city or neighborhood names naturally, and maintains accurate business listings (NAP consistency).
- This helps voice assistants connect users with your business based on proximity and relevancy.
- Aim for Featured Snippets
- Voice assistants often pull answers from Featured Snippets. To capture this, provide direct, short responses at the top of your pages (20–40 words), followed by detailed explanations. Use lists or quick definitions where possible.
- Ensure fast, mobile-first performance
- Most voice queries are made on smartphones or smart devices. Your site should load quickly (ideally under 3 seconds), be responsive on all devices, and support click-to-call or map functionalities for seamless user interaction.

Common Keyword Research Pitfalls
Even experienced marketers fall into some sneaky traps. Here are a few to watch out for:
- Neglecting long-tail keywords: Overlooking specific, lower-volume phrases means missing out on highly targeted traffic and easier wins.
- Relying solely on one keyword tool: No single tool captures the full picture; using multiple sources uncovers more opportunities and reduces blind spots.
- Failing to analyse competitors: Ignoring what’s working for others can leave valuable gaps in your strategy and allow competitors to dominate.
- Over-optimising for keywords: Stuffing content with keywords can harm readability, user experience, and even trigger search engine penalties.
- Not aligning keywords with the customer journey: Using the wrong keywords for the wrong stage (awareness, consideration, decision) leads to poor engagement and conversions.
- Ignoring negative keywords in PPC campaigns: Failing to exclude irrelevant terms wastes ad spend and skews performance data.
- Overlooking on-site search data: Missing out on the actual terms users search for on your website can result in lost insights and content gaps.
- Disregarding seasonality and trends: Not accounting for fluctuations in search demand can cause missed opportunities during peak periods.
- Assuming search volume equals value: High search volume doesn’t always mean high intent or profitability; context and relevance matter more.
- Not tracking and measuring results: Without ongoing analysis, it’s impossible to know what’s working or where to improve your keyword strategy.
Tactical Tips to Speed Your Workflow
- Build reusable keyword sheets with formulas for automated filtering.
- Schedule regular refreshes (quarterly or per product season).
- Ask real customers how they describe their problems—don’t just guess.
- Keep an eye on competitor ‘gap’ terms: where they rank but you don’t.
- Integrate voice search queries (“How do I”, “Where can I find…”).
Sample Keyword Research Roadmap
Below is a simplified workflow you can tweak for your projects:
| Step | Task | Tool/Source |
|---|---|---|
| Define goals | Set conversion, lead gen, traffic targets | Internal |
| Brainstorm seeds | List core products/services, synonyms | Customer chats, forum |
| Generate ideas | Extract bulk keyword suggestions | Ahrefs, GKP, ChatGPT |
| Segment by intent | Tag keywords: info, nav, trans, comm | Sheet/manual |
| Vet for volume/trends | Filter for viable traffic, spot rising trends | SEMrush, Trends |
| Manual SERP analysis | Review top results for each keyword | Google search |
| Prioritise, map, plan | Build plan by difficulty vs. opportunity | Sheet/Asana |
| Create and publish | Write content targeting mapped keywords | CMS |
| Review and revise | Monitor, tweak, repeat | GSC, Analytics |
Mindset for Success
The best keyword researchers in 2025 are agile: ready to respond when data shifts, but still strategic in building for the long term. Combining intuition, analytical rigour, and a dash of creativity, they help brands remain visible, readable, and trustworthy. Agencies like Webzilla, a leader in SEO New Zealand, exemplify this approach—using data-driven strategies and local insights to help clients stay ahead in an increasingly competitive search landscape. As search and content continue to intertwine in new ways next year, the smart money is on those who keep learning, testing, and never see keyword research as ‘done.’ That’s how new opportunities keep appearing, while old methods fade into the rear mirror.

