Types of Search Intent You Must Know for SEO
Types of Search Intent You Must Know for SEO
Most SEO wins start long before you write a headline or build a link. They begin with a clear view of what the searcher really wants. Search intent shapes the SERP, the content that ranks, and the actions users take once they land. When you match it precisely, engagement rises and ranking becomes simpler. Miss it and every other tactic feels like pushing uphill.
Why search intent sits at the heart of SEO
Google’s goal is simple, return results that satisfy the user. To do that, it increasingly interprets the purpose behind a query and reorders results to favour the content type most likely to meet that goal. That is why a page perfectly aligned to intent can outrank stronger domains that miss the mark.
Beyond rankings, intent alignment drives the metrics that matter. Pages that answer informational queries hold attention and earn natural links. Pages built for action convert. Metadata that signals the right intent attracts the right clickers, lifting CTR and filtering out the wrong traffic. The compound effect is better performance across the board.
It also simplifies content planning. Once you classify a keyword’s intent, you can pick the correct format, structure the page, select the right schema, and set realistic KPIs. Effort stops being spread thin and starts compounding around searcher needs.
The core intent types you will meet
The classic model includes informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial research. Many teams also track local intent. Here is a practical snapshot to align your strategy.
| Intent | What the searcher wants | Example queries | Typical SERP features | Winning content format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informational | Learn a fact, process, or concept | how to tie a tie, what is GA4, symptoms of flu | Featured snippets, Knowledge Panel, People Also Ask, videos | Explainers, how to guides, FAQs, step by step articles, video transcripts |
| Navigational | Reach a specific site or page | facebook login, Xero pricing, NZTA road closures | Brand site at position 1, sitelinks, brand panel | Brand landing pages, clear nav, fast load, schema for sitelinks |
| Transactional | Complete an action like buy or sign up | buy iPhone 15, order pizza near me, discount flights Auckland to Bali | Shopping units, product carousels, category pages, coupons | Product pages, category pages, comparison widgets, clear CTAs, trust badges |
| Commercial research | Compare products or services with intent to buy later | best DSLR camera 2025, iPhone 15 vs Pixel 9, Canon G7X review | Roundups, reviews, star ratings, Q&A, long listicles | Buying guides, comparison tables, pros and cons, review hubs |
| Local | Find nearby businesses or services | dentist Ponsonby, coffee near me, plumber Wellington | Map pack, Google Business Profile cards, reviews, directions | Local landing pages, service pages per suburb, GBP optimisation, NAP consistency |
A quick way to check your assumption is to look at the first page. If you see mostly product and category pages for a keyword, the search intent is almost certainly transactional. If you see roundups and reviews, you are looking at commercial research.

Keyword modifiers that hint at intent
Modifiers are not perfect, but they are reliable signals that help triage large keyword lists.
Informational modifiers include terms like how, what, why, guide, tutorial, tips, examples, checklist, ideas, symptoms, causes, benefits, drawbacks, meaning, and definition. These keywords signal users seeking knowledge, explanations, or step-by-step instructions.
Navigational modifiers often feature brand names, product names, login, dashboard, contact, support, and pricing. Users searching with these terms are typically looking to reach a specific website or complete a particular task related to a known brand or service.
Transactional modifiers are words such as buy, purchase, order, coupon, discount, deal, book, subscribe, sign up, and free trial. These indicate strong purchase intent, with users ready to take action or looking for the best deal.
Commercial research modifiers include best, top, vs, compare, review, alternatives, for [use case], and under [price]. These keywords are used by users comparing options, reading reviews, or narrowing down choices before making a decision.
Local modifiers are terms like near me, open now, [suburb] [city], directions, phone number, and map. These signal intent to find local businesses, services, or information relevant to a specific geographic area.
Use these signals to label keywords at scale, then validate by inspecting the SERP to ensure the intent matches the results Google is serving. This approach streamlines keyword research and helps prioritise content creation based on real user needs.
Reading the SERP like a product manager
Treat the results page as a brief from Google telling you what to build.
- Scan the dominant page types: product, category, guide, checklist, review, forum.
- Note SERP features: Shopping carousel, Map pack, Featured snippet, People Also Ask, videos.
- Check freshness: timestamps across the top results signal a recency need. If results are evergreen, prioritise fundamentals over news.
- Analyse title patterns: words like buy or pricing show transactional tilt, while best or review signal commercial research.
- Open the top five results: map headings, content length, media, internal links, and schema.
If the SERP looks split, intent is mixed. Plan either a hub and spoke structure or separate assets that each match a clear slice of the demand.
Designing content that matches intent
Intent is the foundation that determines the ideal format, layout, and calls to action for any web page. To truly meet users where they are in their journey, it’s crucial to design content that aligns with their specific needs and expectations at each stage.
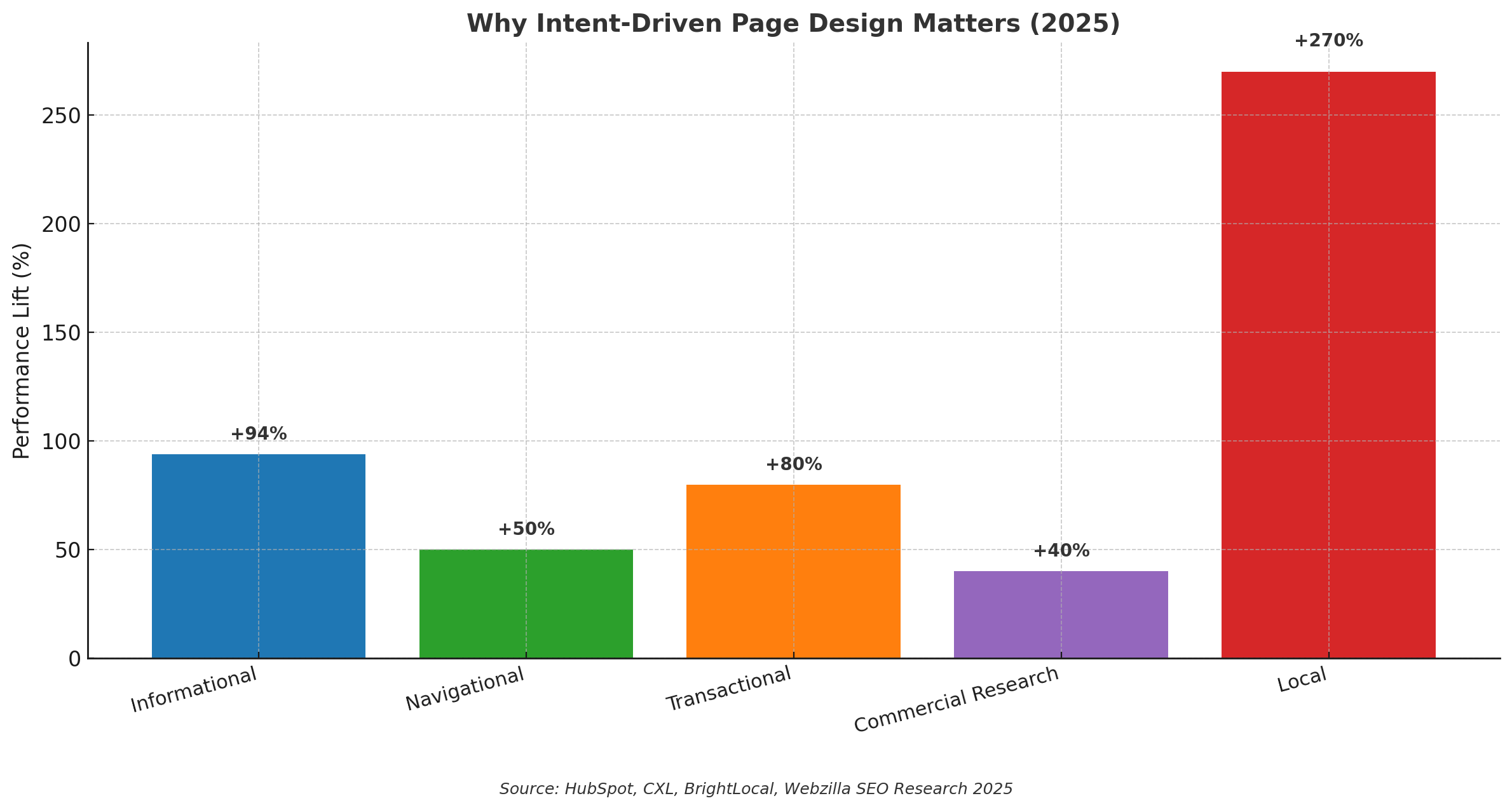
For informational intent, users are seeking answers and clarity. Begin your page with a direct, concise answer to the core question, as this approach increases the likelihood of capturing featured snippets and improves user satisfaction. Follow up with well-structured, scannable sections that allow readers to dive deeper as needed. Incorporating step-by-step guides, diagrams, or short explainer videos can boost engagement—pages with visual aids see up to 94% more views, according to HubSpot. Where relevant, implement FAQ schema to enhance visibility in People Also Ask results. Calls to action here should be soft and contextual, such as offering a downloadable checklist, interactive calculator, or a free email course, which can increase lead generation without disrupting the user’s research flow.
Navigational intent is all about helping users reach a specific destination with minimal friction. Pages should load quickly and make the sought-after action—like accessing pricing, logging in, or contacting support—immediately obvious. Clean headings that match brand queries in both the H1 and title tags reinforce relevance and trust. Where appropriate, adding sitelinks search box schema can streamline navigation, especially for larger brands. Research shows that reducing steps to task completion can improve conversion rates by up to 50%.
Transactional intent demands a focus on conversion. Place critical information such as price, availability, delivery options, returns policy, and social proof (like reviews and ratings) above the fold, as 80% of users make purchase decisions based on what they see without scrolling. Enhance listings with product schema, review stars, and real-time stock status to stand out in search results. Keep forms short to reduce abandonment, and offer multiple buying paths—such as online purchase, click and collect, or phone orders—to cater to different preferences and increase sales.
For commercial research, users are comparing options before making a decision. Lead with a clear verdict or shortlist, backed by a transparent methodology that explains how products or services were evaluated. Use comparison tables, pros and cons lists, and scenarios tailored to different use cases or budgets. Strong internal links to relevant product or category pages guide users seamlessly to the next step, increasing the likelihood of conversion. According to CXL, well-structured comparison content can increase time on site by up to 40%.
Local intent requires hyper-relevant, location-specific content. Create dedicated pages for each city or suburb, including consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) details, business hours, parking information, and local testimonials to build trust. Embedding a map and adding authentic photos help users visualize your location, while the LocalBusiness schema improves local search visibility. Keeping your Google Business Profile up to date and actively earning reviews can drive steady growth in local rankings and customer engagement—businesses with more than 50 recent reviews see up to 270% more clicks from local search results.
By aligning every aspect of your page with user intent, you not only enhance SEO performance but also create a seamless, satisfying experience that moves users confidently toward their goals.
Mapping intent to the funnel and metrics
Intent aligns closely with the stages of the buying cycle, and setting clear goals and KPIs for each stage is essential for measuring true SEO success. For informational intent, which targets users in the awareness and education phase, the primary objectives are to maximise organic reach, grow your email list, and drive assisted conversions. Key metrics here include impressions, featured snippet wins, time on page, scroll depth, and newsletter opt-ins. According to industry benchmarks, pages optimised for informational queries can increase organic impressions by up to 60% and often serve as the top entry point for new users. Even if these pages don’t convert directly, their value lies in nurturing leads and building brand authority.
During the commercial research or consideration stage, the focus shifts to generating product interest and facilitating comparisons. Goals include increasing the number of product comparisons viewed and demo requests submitted. Metrics such as click-through rate (CTR) from the SERP, interactions with comparison tables, outbound clicks to product pages, and assisted conversion value provide a clear picture of engagement. Research shows that interactive comparison content can boost product page visits by 30% and significantly influence purchase decisions.
Transactional intent corresponds to the decision phase, where users are ready to buy, book, or subscribe. Here, the main goals are driving sales, bookings, and subscriptions. Metrics like conversion rate, average order value, basket abandonment rate, and checkout speed are critical. Data from Shopify reveals that optimising for transactional intent can increase conversion rates by up to 25%, especially when friction is minimised and trust signals are prominent.
Navigational intent typically involves returning users or those curious about your brand. The aim is to facilitate task completion, increase login rates, and reduce support requests. Success can be measured by task success rates, internal search exits, and support ticket volume. Streamlining navigation and providing direct access to key actions can reduce support queries by up to 40%, according to Zendesk.
For local intent, the goal is to drive real-world actions such as calls, direction requests, bookings, and in-person visits. Metrics include Google Business Profile (GBP) views, call clicks, direction requests, and local rankings in the map pack. Businesses that rank in the top three of the map pack receive up to 70% of local clicks, highlighting the importance of optimising for these signals.
Ultimately, it’s vital to tie each page’s performance to its underlying intent. For example, a well-crafted how-to guide that increases newsletter signups and assists in revenue generation is fulfilling its purpose, even if it doesn’t drive direct conversions. By aligning goals and KPIs with user intent at every stage, you ensure your SEO strategy delivers measurable value across the entire customer journey.
Handling mixed and ambiguous intent
Some keywords attract multiple intents. Think iphone 15 where users may want specs, reviews, or to buy. Your choices:
- Build a hub page that addresses the main paths with clear sections and jump links, then link to deep pages for each sub intent.
- Split the keyword into separate pages and target long tail modifiers, for example iphone 15 specs, iphone 15 review, buy iphone 15 NZ.
- Let the SERP guide your choice. If the top results are hubs, build a hub. If they are split, choose the slice where you can be strongest and support it with internal links.
Avoid cannibalization. Ensure each page has a distinct angle, title, and primary keyword set.
Local intent in Aotearoa New Zealand
Local search is a unique discipline within SEO, shaped by its own set of signals and user expectations. Success in this space hinges on attention to detail and a deep understanding of what local customers value. One of the most critical elements is your Google Business Profile. Ensuring your Name, Address, and Phone Number (NAP) are consistent across your website, directories, and social media profiles is essential—studies show that inconsistent NAP information is a leading cause of lost local rankings and customer trust. Enhance your profile by uploading authentic photos, selecting accurate service categories, listing products, and actively using the Q&A feature. Regularly posting updates about promotions or seasonal hours can increase engagement by up to 40%. Responding to every review, whether positive or negative, in a timely and friendly manner not only builds credibility but also encourages more customers to leave feedback—businesses that reply to reviews see up to 12% more reviews on average.
Location pages are another cornerstone of effective local SEO. Avoid generic, boilerplate content; instead, craft unique copy that references nearby landmarks, suburbs, and services tailored to each area. For example, mentioning local pricing, after-hours options, and emergency contact information is especially important for industries like trades and healthcare, where urgency and trust are paramount. Incorporate structured data to help search engines understand your local relevance, and use internal links from city and suburb hub pages to strengthen your site’s architecture. Embedding a Google Map not only helps users find you but also signals local relevance to search engines.
Given that over 60% of local searches happen on mobile devices, optimising the mobile experience is non-negotiable. Features like tap-to-call, one-click directions, and lightning-fast page loads are vital, as many users are searching while on the move. Make essential information—such as opening hours, parking availability, and accessibility—immediately visible to reduce friction and improve conversion rates.
Finally, cultural context is crucial in New Zealand’s diverse market. Use NZ English and be mindful of local nuances in spelling and phrasing. If your audience includes te reo Māori speakers, consider incorporating bilingual headings or a glossary of key terms to foster inclusivity and trust. According to recent surveys, businesses that embrace local culture and language see higher engagement and loyalty from their communities. By weaving these elements together, you can create a local search presence that is both discoverable and deeply resonant with your target audience.
A simple workflow for intent first SEO
Use a repeatable process that keeps teams aligned.
- Gather keywords from Search Console, paid search, competitor gaps, and customer interviews.
- Label each keyword with a draft intent using modifiers.
- Validate by inspecting the SERP. Record dominant page types and features.
- Choose the correct format and define the page’s job to be done.
- Outline with headings that mirror the SERP’s successful structure, then add your unique value.
- Implement on page signals: titles, meta, schema, internal links, media.
- Set KPIs by intent stage and ship.
- Review engagement and conversion data, refine structure and CTAs, and iterate.
Document intent decisions in your content brief. This avoids scope creep and keeps copy, design, and development pulling in the same direction.
Common pitfalls and how to fix them
One common pitfall in SEO is publishing content in the wrong format for the user’s search intent. For example, creating a product page to target a “best of” query, or writing a blog post when users are ready to buy, leads to poor rankings and low engagement. Research shows that aligning your content format with what currently ranks in the SERP can increase your chances of reaching page one by over 50%. If you find a mismatch, it’s crucial to either rebuild the page to match the dominant SERP format—such as switching from a product page to a comparison guide—or retarget the page to a keyword that better fits its existing format.
Another frequent mistake is prioritising keyword search volume over intent quality. Chasing high-traffic keywords may bring visitors, but if those users bounce and never convert, the effort is wasted. Data from HubSpot indicates that businesses focusing on intent-driven keywords see conversion rates up to three times higher than those optimising for volume alone. The solution is to prioritise keywords where your business can genuinely satisfy the user’s intent and drive profitable actions, even if the search volume is lower.
Thin commercial pages are also a widespread issue, especially in affiliate and review-driven niches. Lists like “top ten” products often lack original research, testing, or clear criteria, which undermines trust and authority. To stand out, it’s essential to “show your work”—explain your methodology, include original photos, present test data, and provide context for your recommendations. According to Backlinko, in-depth reviews with transparent testing processes are 2.5 times more likely to earn backlinks and rank higher.
Ignoring SERP features is another missed opportunity. Many sites overlook optimising for featured snippets, adding schema markup, or publishing videos when the results page is video-heavy. Yet, capturing a featured snippet can boost click-through rates by up to 30%, and schema markup increases the likelihood of enhanced search listings. To capitalise on these opportunities, optimise your summaries for snippet capture, implement relevant schema, and create short supporting videos where appropriate.
Finally, keyword cannibalisation—where multiple pages target the same intent and keyword set—can dilute your rankings and confuse search engines. SEMrush reports that resolving cannibalisation issues can improve organic traffic by up to 20%. The best approach is to consolidate overlapping pages into a single, stronger asset, or differentiate each page by use case, audience segment, or price band to ensure clear targeting and maximise your site’s authority.
Practical patterns that work
To boost clarity and drive more clicks from search, it’s essential to tailor your page elements to both user intent and Google’s evolving SERP features. Crafting titles that directly match search intent is a proven strategy: for informational queries, use formulas like “How to [achieve outcome] in [timeframe] without [common pain],” which can increase click-through rates by up to 20% according to recent A/B tests. For commercial research, titles such as “Best for [use case] in [year] with test results” signal depth and recency, both of which Google and users favour. Transactional titles should highlight buying options, pricing, delivery, and returns—key factors that 70% of online shoppers consider before clicking. For local searches, including the service, suburb, pricing, hours, and online booking options in the title can significantly improve local pack visibility. Navigational queries benefit from straightforward titles like “[Brand] pricing, features, and plans,” making it easy for users to find exactly what they need.
Optimising your introductions for snippet capture is another high-impact tactic. Start with a concise, one- or two-sentence definition or answer to the user’s query. Immediately follow with a numbered list of steps or a short comparison table. This structure not only appeals to Google’s featured snippet algorithm but also helps users quickly find the information they’re seeking. Data shows that pages structured for snippets can see up to a 30% increase in organic traffic.
Comparison tables are especially effective for commercial and review content. Design your tables with clear columns for model, key features, pros, cons, price in NZD, and “best for” recommendations. Keep the layout scannable and honest, and link each row to a deeper review or product page. Well-structured tables can improve user engagement and time on page, with studies showing a 15% higher conversion rate when comparison tables are present.
On-page elements should follow a comprehensive checklist to maximise both SEO and user experience. Ensure your H1 mirrors the primary intent of the page, and use descriptive subheadings that align with People Also Ask themes to capture additional long-tail traffic. Implement schema markup appropriate to the page type—such as Product, FAQ, or LocalBusiness—to enhance your search listings with rich results. Internal links should guide users to the next logical step in their journey, increasing site depth and reducing bounce rates. Finally, place trust signals—like reviews and testimonials—strategically near calls to action on buy pages, as this can lift conversion rates by up to 35%. By systematically applying these templates and best practices, you can create content that not only ranks but also resonates with and converts your target audience.
Measuring success without getting lost in averages
Averages hide the truth. Break out reporting by intent.
- Informational pages should grow impressions, featured snippets, and assisted conversions. Track micro conversions like downloads or email signups.
- Commercial research pages should lift CTR, drive engagement with tables and toggles, and move users to product pages.
- Transactional pages should improve conversion rate, checkout speed, and revenue. Watch abandonment by device.
- Local pages and profiles should lift calls, bookings, and direction requests. Monitor map pack rankings by suburb on mobile.
If a page falls short, ask a simple question, did we satisfy the searcher’s goal better than the current top results. The fix usually sits in structure, clarity, or format, not in word count.
Advanced signals to watch
- Freshness sensitivity: queries that spike with product launches or seasonal trends need timely updates. Maintain evergreen pages and add a short updates section with the latest changes.
- Entity coverage: for complex topics, cover the key entities and attributes that users expect. Use headings that mirror how experts describe the space, then support with plain language explanations.
- Intent shifts after core updates: some keywords swing from informational to commercial research or vice versa. Recheck the SERP after major updates and adjust the page’s angle or split content if needed.
- Tool support: use intent labels in tools as a starting point, then confirm manually. Filter by SERP features to spot transactional and local clusters quickly.
Keep an intent map for your site and revisit it quarterly. When your content and your audience’s purpose stay aligned, everything else in SEO gets easier.

