
What is Google Ads and How it Works
What is Google Ads and How it Works
So many everyday online experiences are quietly shaped by systems running in the background, connecting people to services, ideas, and products. Google Ads is one of the leading forces in this space, quietly fuelling a large portion of the internet’s economy, and bringing marketers and audiences together in a way that feels personal, calculated, and, often, seamless. From the small coffee shop aiming to increase its morning rush to the tech startup targeting clients across the globe, this advertising platform serves as a fundamental tool for growing new audiences and driving business goals.
At its heart, Google Ads allows organisations of every size to control when, where, and how their messages appear across Google’s vast landscape — from search results to videos, shopping listings, maps, and far beyond. While it might appear complex on the surface, once you understand the underlying principles, its flexibility and precision make it a vital engine for anyone with a product, a service, or a story to tell.
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is Google’s online advertising platform that enables businesses to display ads across Google’s search results, YouTube, and a vast network of partner websites. With Google Ads, advertisers can reach potential customers precisely when they’re searching for products or services, making it one of the most effective tools for driving targeted traffic and generating leads.
At its core, Google Ads operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning you only pay when someone clicks on your ad. The platform allows you to set your own budget, choose specific keywords to target, and tailor your ads to reach the right audience based on location, interests, and more.
Businesses use Google Ads to:
- Increase visibility and brand awareness
- Drive more qualified traffic to their websites
- Generate leads and sales efficiently
- Reach customers at the exact moment they’re searching for relevant solutions
- most importantly google ads provide measurable result that tradition marketing can’t
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, Google Ads offers flexible options to help you achieve your marketing goals and grow your business online.
The Evolution from Google AdWords to Google Ads
Google Ads was originally launched as Google AdWords in 2000, marking the beginning of Google’s journey into online advertising. For nearly two decades, Google AdWords became synonymous with pay-per-click advertising, allowing businesses to bid on keywords and display ads in Google’s search results and partner sites.
In July 2018, Google rebranded AdWords as Google Ads. This change reflected the platform’s evolution beyond just keyword-based search advertising. Today, Google Ads encompasses a wide range of ad formats and channels, including display ads, video ads on YouTube, app promotion, shopping ads, and more.
While the core principles remain the same—helping businesses connect with customers at the right moment—the rebranding to Google Ads signifies a more unified and versatile advertising solution. The platform now offers a streamlined interface, improved campaign management tools, and expanded reach across Google’s entire ecosystem.
Key Differences:
- Google AdWords focused primarily on search and display advertising.
- Google Ads includes all previous features plus new options for video, app, and shopping campaigns.
- The rebranding introduced a more user-friendly experience and broader targeting capabilities.

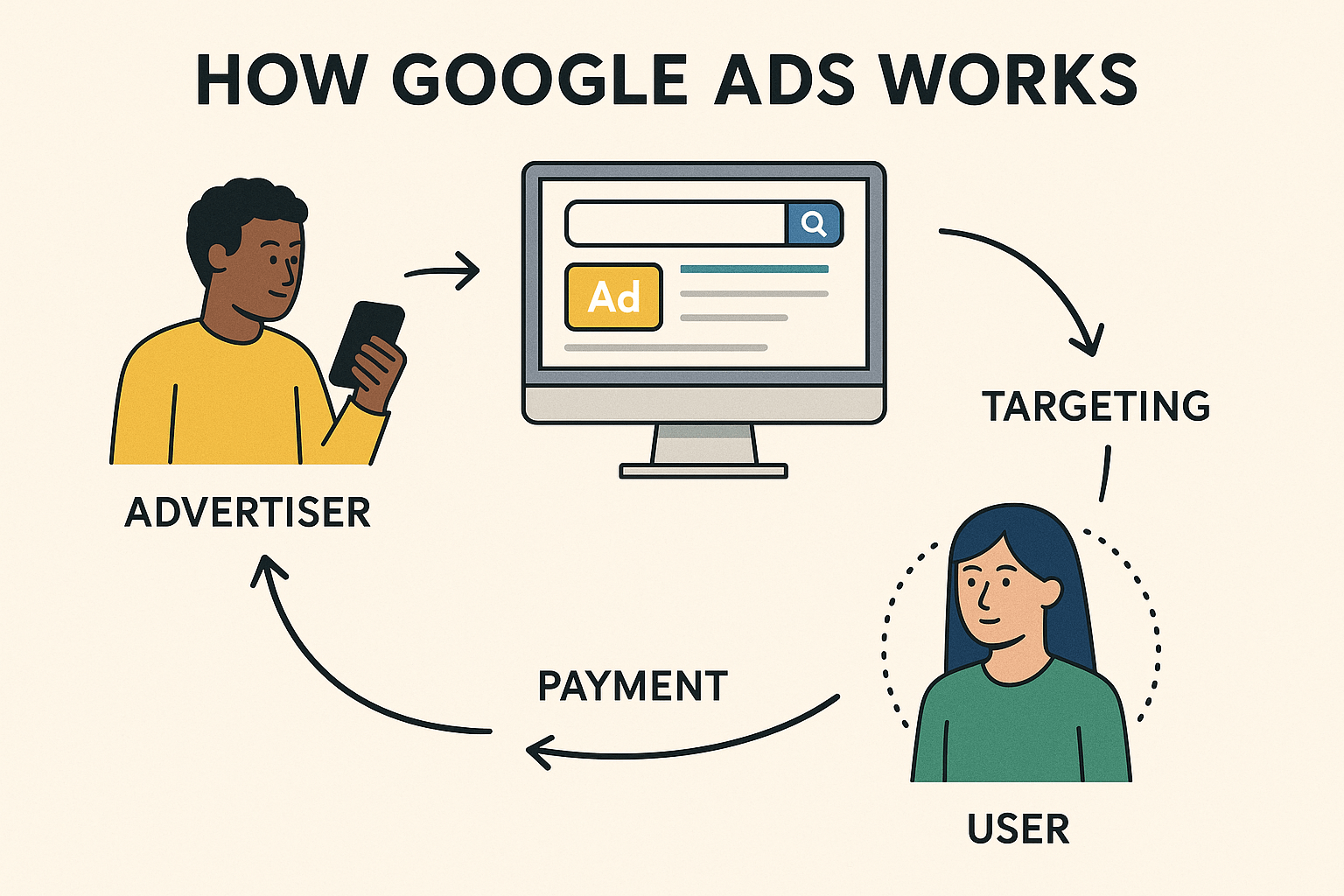
How Google Ads Works
Picture every time you type a search query into Google. Within milliseconds, an almost invisible auction occurs behind the scenes. Businesses bid against one another for the chance to be one of the handful of sponsored links you’ll notice at the top (and sometimes the bottom) of your results page. These aren’t just blunt-force transactions; they’re meticulously crafted, backed by a world-leading algorithm that weighs not only how much was bid, but also how relevant the ad is to your search and even how effective that ad was for similar searchers in the past.
If you’re wondering why your ads might not always appear when you search, read our guide on why you might not see your Google Ads.
But Google Ads stretches well beyond those modest blocks at the top of your search results. It includes:
- Display ads on millions of websites and apps
- Sponsored video spots on YouTube
- Shopping ads that showcase products with rich visuals
- Targeted promotions on Google Maps
Each of these placements allows advertisers to reach specific audiences in the context that fits best for their goals—whether that’s catching people who are in the mood to browse, ready to make a decision, or looking for inspiration.
Personalized Content and Ads in Google Ads
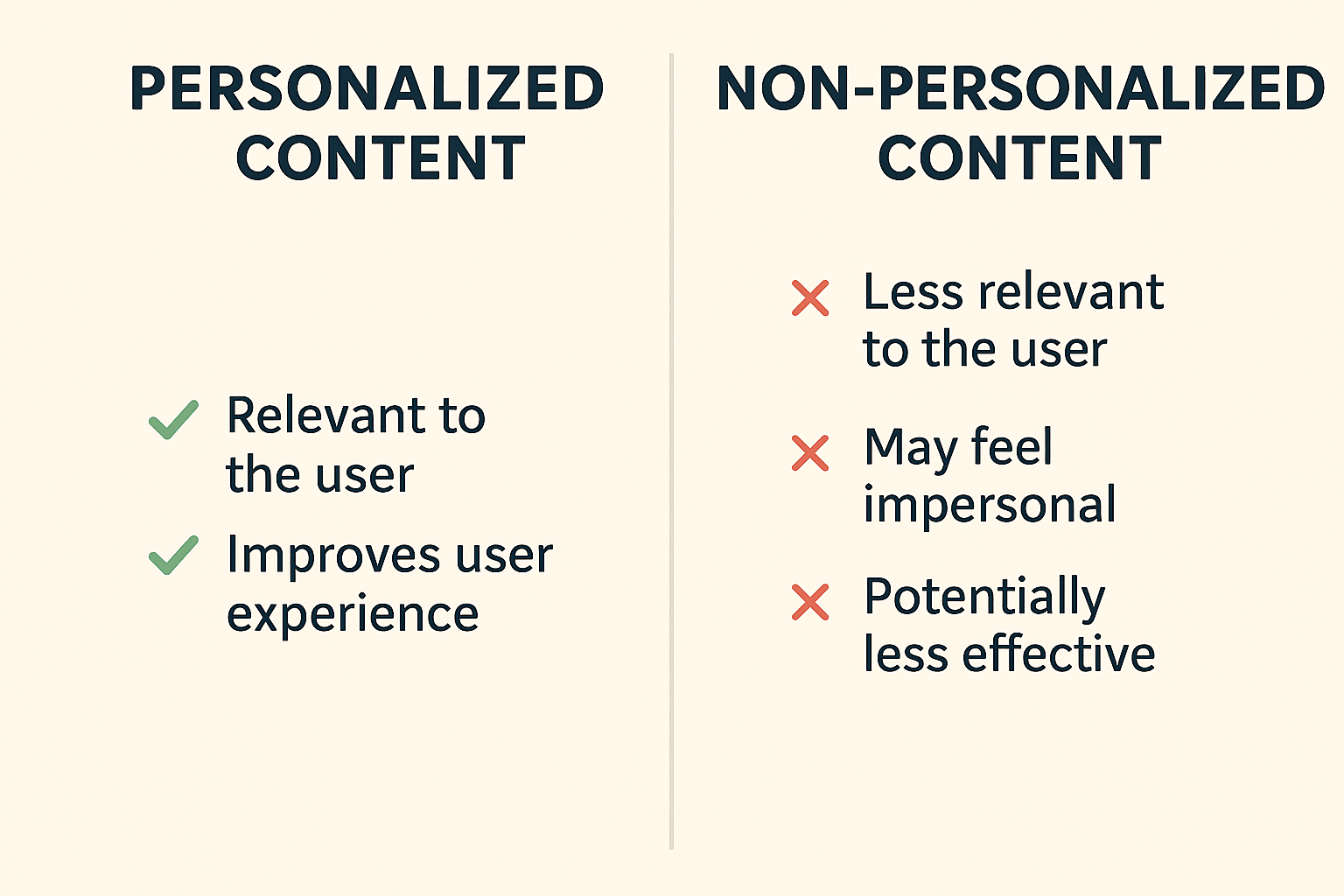
Personalized Content
Google Ads leverages user data—such as search history, browsing behaviour, and interests—to deliver personalised content. This means that when users interact with Google’s platforms, the ads and content they see are tailored to their unique preferences and online activities. For example, someone who frequently searches for hiking gear may see ads for outdoor equipment stores or adventure travel packages.
Personalised content enhances the user experience by making ads more relevant and engaging. For advertisers, this targeting increases the likelihood of reaching potential customers who are genuinely interested in their products or services, leading to higher click-through and conversion rates.
Personalized Ads
Personalised ads are a core feature of Google Ads, allowing advertisers to deliver messages that resonate with individual users. By analysing data such as location, device, demographics, and past interactions, Google Ads enables businesses to create highly targeted campaigns. For instance, a local café can show breakfast specials to nearby users during morning hours, or an online retailer can retarget users who previously visited their website but didn’t make a purchase.
The difference between personalised and non-personalised ads lies in the level of targeting. Personalised ads use detailed user data to tailor messages, while non-personalised ads are shown based on general factors like the content of the website or broad location.
Non-Personalized Content
Non-personalised content refers to ads and recommendations that are not based on a user’s individual data or behaviour. Instead, these ads are targeted using more general information, such as the context of the website or the user’s rough geographic location. Non-personalised ads are often used to comply with privacy regulations or user preferences, especially in regions with strict data protection laws.
While non-personalised ads may be less relevant to individual users, they still play an important role in reaching broader audiences and maintaining compliance with privacy standards. For advertisers, this approach may result in lower engagement rates compared to personalised campaigns, but it ensures that advertising remains accessible and respectful of user privacy choices.
Understanding Ad Rank
Ad Rank is a crucial factor in Google Ads that determines where your ad appears on the search results page and whether it shows up at all. It’s not simply about how much you bid—Ad Rank is calculated using a combination of your bid amount, the quality of your ads and landing page, the expected impact of ad extensions, and other relevance factors.
How Ad Rank is Calculated
Ad Rank = Bid Amount × Quality Score × Expected Impact of Extensions and Other Factors
- Bid Amount: The maximum amount you’re willing to pay for a click.
- Quality Score: Google’s assessment of the relevance and quality of your ad, keywords, and landing page.
- Ad Extensions & Other Factors: Additional information you include with your ad, such as phone numbers or site links, which can improve user experience.
Why Ad Rank Matters
Ad Rank determines:
- Ad Position: Higher Ad Rank means your ad appears in a more prominent position, often at the top of the search results.
- Eligibility: If your Ad Rank is too low, your ad may not show at all.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): A higher Quality Score can lower your actual CPC, meaning you pay less for better positions.
Example
Suppose two advertisers are competing for the same keyword:
- Advertiser A bids $2.00 and has a high Quality Score.
- Advertiser B bids $3.00 but has a lower Quality Score.
If Advertiser A’s overall Ad Rank is higher due to better ad quality and relevance, their ad could appear above Advertiser B’s, even with a lower bid.
Focusing on improving your Quality Score and using effective ad extensions can help you achieve a higher Ad Rank, leading to better visibility and more efficient ad spend.
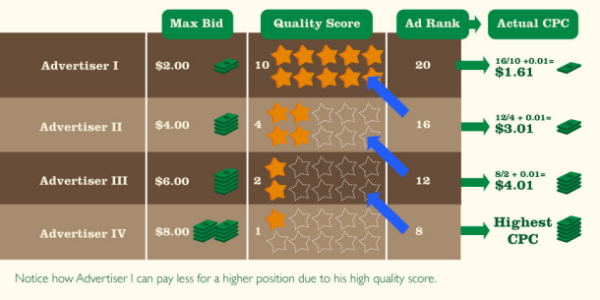
Image Source: Search Engine Land
Different Types of Campaigns
Google Ads isn’t just a single monolithic entity. It’s a toolbox with several distinct compartments. The most common campaign types include:
| Campaign Type | Where Ads Appear | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Search | Google search results pages | Immediate intent, direct sales |
| Display | Partner websites, apps, and Gmail | Raising awareness, broad reach |
| Video | YouTube and Google Video partners | Storytelling, brand building |
| Shopping | Google Shopping and search results | Retail, product showcase |
| App | Across Google’s properties, apps, YouTube, Play | App downloads and engagement |
| Local | Google Maps, Search, partner sites | Driving in-person visits |
| Smart | Automated across Google properties | Small businesses, simplicity |
| Performance Max | All Google channels (Search, Display, YouTube, Gmail, Maps, Discover) | Maximising conversions with automation across channels |
Each campaign type comes with its own strategies and best practices. Someone launching an online shop might focus on Shopping campaigns, while a tourism provider would see particular value in Display or Video options to inspire would-be travellers.
Google Shopping AdsFor actionable strategies about google shopping ads, see our guide on how to optimise Google Shopping Ads.
Keyword Targeting and Audiences
Perhaps Google Ads’ most distinguishing feature is its focus on intent. Rather than simply spraying ads indiscriminately, it lets you zero in on users at the precise moment they’re signalling interest. This happens primarily through keywords. Advertisers select a set of keywords that match the words and phrases people are likely to search for, and ads are triggered when those terms are entered.
But keywords are just the beginning. Google allows further targeting by demographics, interests, device type, location, time of day, and even custom-defined audiences. For example:
- A bakery can run ads only within a specific radius, targeting people looking for “fresh bread near me”.
- An online clothing store might target recent visitors to the site, or extend to lookalike audiences who have similar browsing behaviours.
This blend of keyword and audience targeting enables both precision and scalability, letting businesses control every dollar spent.

Pay-for-Performance Model
A major reason Google Ads continues to be so popular is its pricing model. Most campaigns operate on a pay-per-click (PPC) model — you’re charged only when someone actually clicks on your ad, not simply for the ad appearing. For some campaign types (like video), you might pay for views or other engagement actions.
For a comprehensive breakdown of costs, see our guide on how much Google Ads costs.
This system makes it possible to test, iterate, and optimise campaigns without massive upfront costs. Budget controls are built in, allowing advertisers to set daily, weekly, or monthly limits, and even bid differently for different placements or times of day.
Not everything is about the highest bid, though. Google uses something called Quality Score to rank ads. This metric weighs the expected clickthrough rate, relevance to the user’s query, and the landing page experience. Even if your competitor bids higher, your ad can appear above theirs if your ad is more relevant and useful.
Crafting an Effective Ad
The effectiveness of a Google ad hinges as much on creativity as it does technical precision. Good ads provide clear, compelling reasons for why someone should engage right now rather than later. They’re relevant to the searcher’s intent, honest in their promises, and optimised for mobile screens (given growing mobile usage).
Successful ads typically:
- Use the target keyword naturally within the headline and description
- Include a call to action (“Book now”, “Download today”, “See our deals”)
- Make use of ad extensions (like site links, call buttons, or local addresses) to add further value and context
- Lead to landing pages that match the ad’s promise
Testing different combinations and measuring the resulting performance is central to refining and improving success over time.
Ad Copywriting Best Practices
Crafting effective ad copy is both an art and a science. The right words can capture attention, evoke emotion, and drive action—all within a limited character count. Here’s how to elevate your Google Ads copywriting:
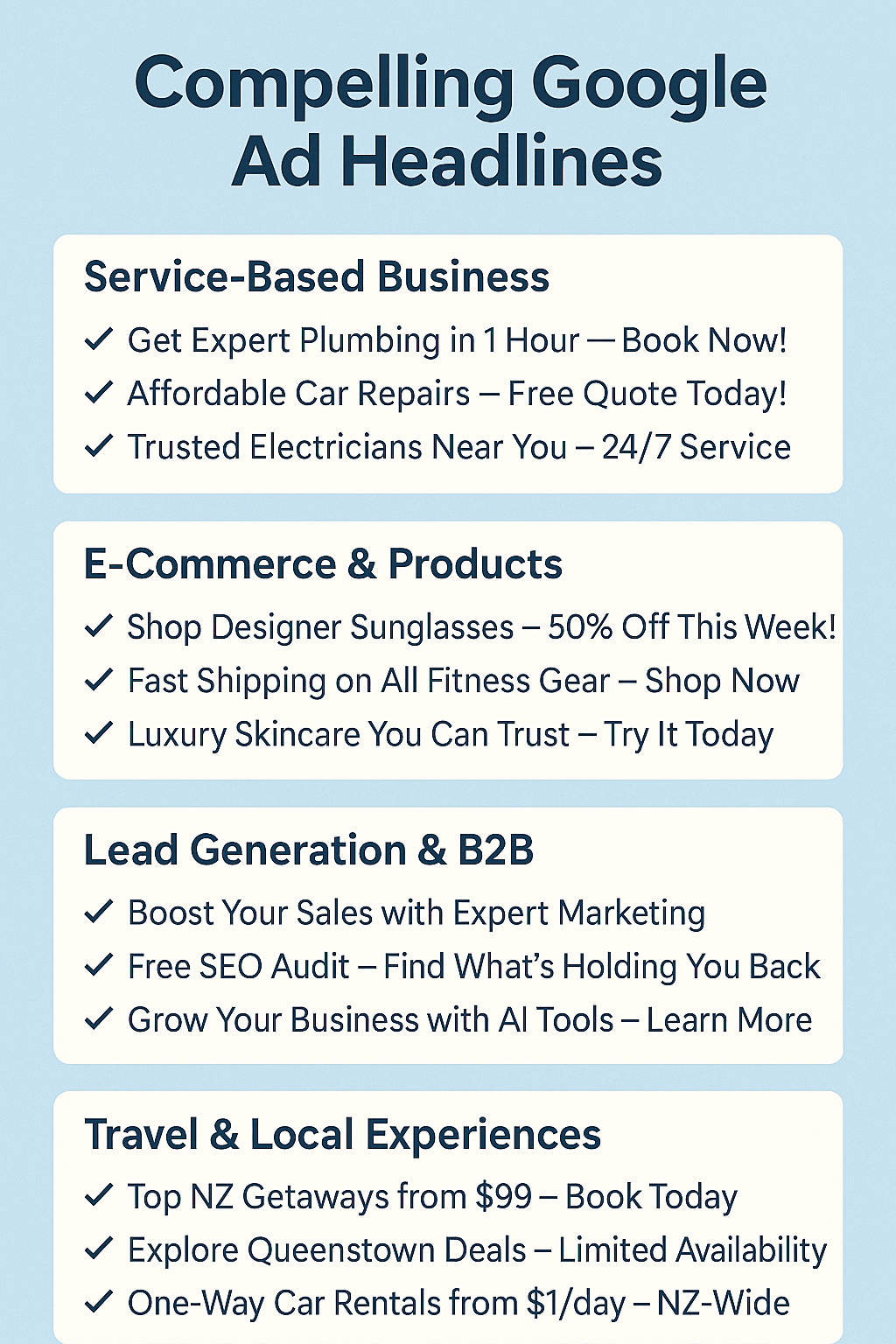
1. Write Compelling Headlines
- Be Clear and Direct: Your headline should immediately communicate what you offer. Avoid jargon and focus on clarity.
- Include the Keyword: Integrate your target keyword naturally to boost relevance and Quality Score.
- Highlight Benefits: Focus on what the user gains, not just what you do. For example, “Get Fresh Bread Delivered Daily” is more enticing than “Bakery Delivery Service.”
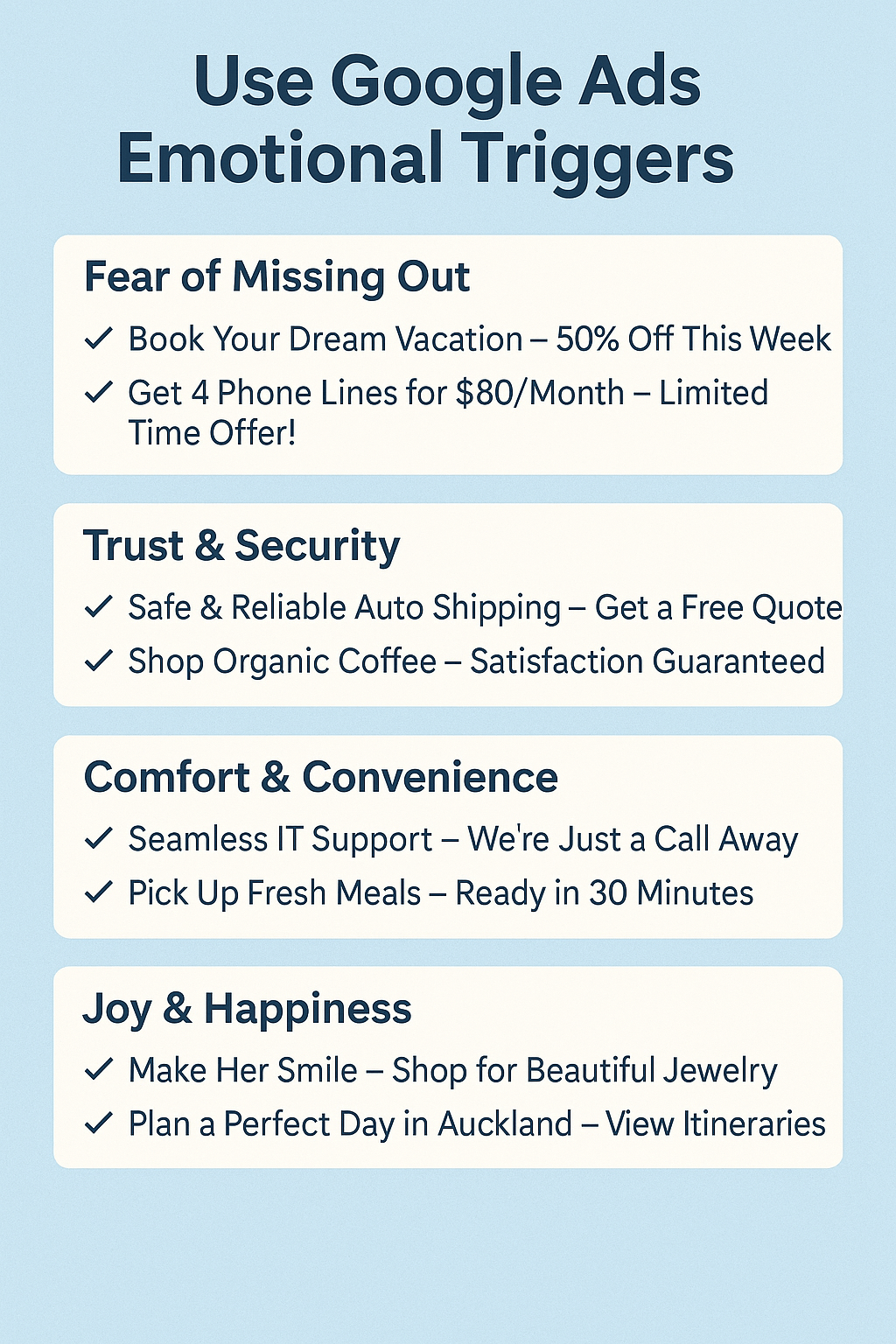
2. Use Emotional Triggers
- Appeal to Aspirations: Use language that taps into your audience’s desires or solves their pain points.
Example: “Transform Your Mornings with Artisan Coffee.” - Create Urgency: Phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Only a Few Left” encourage immediate action.
- Build Trust: Words like “Trusted by Thousands” or “Award-Winning Service” add credibility.
3. Communicate a Strong Value Proposition
- Differentiate: What makes your offer unique? Highlight exclusive features, guarantees, or expertise.
- Be Specific: Use numbers or concrete details.
Example:

4. Include a Clear Call to Action (CTA)
- Guide the Next Step: Use action-oriented phrases like “Book Now,” “Get a Free Quote,” or “Shop the Sale.”
- Match the CTA to Intent: If your ad is for research, try “Learn More.” For purchases, use “Buy Now.”

5. Test and Optimise with A/B Testing
- Experiment: Run two or more versions of your ad with different headlines, descriptions, or CTAs.
- Measure Results: Use Google Ads’ built-in tools to track which version performs best (higher CTR, conversions, etc.).
- Iterate: Regularly update your ads based on data to improve results continually.
Examples of High-Performing Ads
Example 1:
Fresh Bread Delivered Daily
Order by 9am for Same-Day Delivery.
Taste the Difference – Shop Now!
Example 2:
Transform Your Workspace
Award-Winning Office Fitouts for Modern Businesses.
Get a Free Consultation Today!
Example 3 (A/B Test):
- Version A: “Book Your Dream Holiday – Save 15% on All Tours”
- Version B: “Explore Hidden Gems – Limited Time Tour Discounts”
Measurement and Analytics
Google provides a dense toolkit for tracking the performance of campaigns. Advertisers can see what’s working, what isn’t, and adjust in near real-time.
Some of the core metrics include:
- Clickthrough rate (CTR): How often people click after seeing your ad
- Conversion rate: The percentage of clicks that result in an action (sale, lead, signup)
- Cost per click (CPC): How much you’re paying per engagement
- Quality Score: Google’s internal rating of your ad’s relevance and usefulness
This data-driven environment means you’re never flying blind. Well-run campaigns are continually refined in response to changing user behaviour, competitive activity, and business goals.
To dive deeper into evaluating your marketing efforts, check out our guide on how to measure the effectiveness of a digital marketing campaign.
The Broader Impact for Businesses
Businesses worldwide have unique opportunities and challenges. Whether you’re running a small local shop or launching a SaaS product for a global audience, Google Ads enables you to reach both hyper-local and international markets with confidence.
The ability to target by city, country, or even by events means marketing budgets can stretch further and achieve sharp results.
For example, many retailers have coupled Google Ads with a strong Google Business Profile presence. They target mobile searches in their area, providing immediate directions, contact details, and opening hours. In tourism, innovative operators draw travellers at their research phase, weaving unique experiences into the dreaming and planning stages long before bookings are made.
Getting Started
While the technical options can look daunting, entry is straightforward. Google provides a step-by-step onboarding process. To start, you’ll need a Google account, a clear understanding of your main business objective, and a small budget to test the waters.
A simple workflow might look like this:
- Pick your campaign type (e.g. Search or Display)
- Set your daily or monthly budget
- Define your ideal audience (keywords, demographics, locations)
- Write targeted ads with sharp calls to action
- Monitor performance and adjust as you go
There’s no universal blueprint. Success is shaped by learning from real-world data, making tweaks, and trying new angles.
Common Questions
People often raise concerns like:
Isn’t Google Ads too expensive for small businesses? With the right targeting and careful measurement, even modest budgets can have an impact. Many businesses start with just a few dollars a day.
What if I make mistakes? Mistakes are part of the process, but Google’s analytics suite helps you see quickly what’s working and what isn’t. It’s okay to start small, experiment, and refine.
How long until I see results? Campaigns can drive clicks instantly, but meaningful data often builds up over days or weeks as you optimise your targeting and messages.
Do I need to hire an expert? Plenty of businesses run successful campaigns in-house. For those with the time and inclination, Google’s learning resources and support make it very doable.

Bringing It All Together
Learning the mechanics of Google Ads opens a powerful new avenue for nearly any business. Its balance of scale, targeting precision, and measurable results makes it a fixture of the modern marketing toolkit.
The internet has an uncanny ability to shrink distances, find niche audiences, and amplify the local on the global stage. Google Ads stands as one of the key ways entrepreneurs, creatives, and companies can reach exactly the customers they need, at exactly the moment they’re needed. The platform’s impact on commerce and entrepreneurship is only set to deepen.
For anyone with ambition and an idea, now is a ripe time to give Google Ads a proper look. The tools you need are just a few clicks away.
